Fundamentals of Perpetual Futures
Abstract
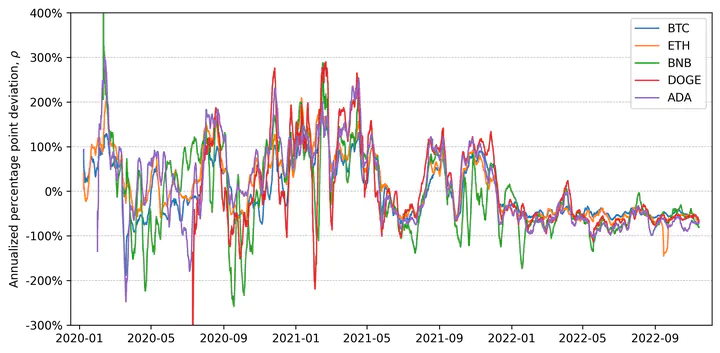
Perpetual futures are the most popular cryptocurrency derivatives. Perpetuals offer leveraged exposure to their underlying without rollover or direct ownership. Unlike fixed-maturity futures, perpetuals are not guaranteed to converge to the spot price. To minimize the gap between perpetual and spot prices, long investors periodically pay shorts a funding rate proportional to this difference. We derive no-arbitrage prices for perpetual futures in frictionless markets and bounds in markets with trading costs. Empirically, deviations from these prices in crypto are larger than in traditional currency markets, comove across currencies, and diminish over time. An implied arbitrage strategy yields high Sharpe ratios.